Transition of compulsory earthquake insurence policy to compulsory disaster insurence policy in Türkiye
Senior Manager, Project Coordination & Field Management
Turkish Catastrophe Insurance Pool
Turkish Catastrophe Insurance Pool, TCIP (& DASK in Turkish) was established in 2000 following the devastating earthquake at Marmara region on 18 August 1999. Although Catastrophe Insurance Law allows TCIP to provide insurance and/or reinsurance cover against Nat-Cat perils, TCIP provides only earthquake insurance coverage for residential dwellings in Türkiye since its establishment.
TCIP became one of the best practices of its kind even with increasing penetration rate which is about 56% for the time being and with the claims handling practices that have been put in to service during the last decade proving its effectiveness in the Kahramanmaraş earthquake on 6 February 2023. The Kahramanmaraş earthquakes affected 11 cities directly where over 13 million citizens lived, being the area of these cities larger than that of many European countries. Some 600,000 claims were submitted to TCIP and almost 95% of them are completed within 8 months’ time.
2021, the year that COVİD-19 pandemic was still in force with all its negative effects, it was also a year that natural disasters were experienced intensely all around the world as well as in Türkiye due to climate change and global warming. Floods and forest fires that occurred throughout Türkiye on summer 2021 brought forward the topic of the scope extension of the Compulsory Earthquake Insurance, which TCIP offers as financial assurance against earthquake, with Nat-Cat perils. TCIP privileged the study on integrating natural perils, following the information letter of the Insurance and Private Pension Regulation and Supervision Agency (SEDDK) shared with the public.
TCIP is now advancing toward a more comprehensive disaster insurance framework to address the evolving risk landscape and enhance community resilience. This shift aims to establish a compulsory multi-hazard disaster insurance program. The proposed framework extends coverage beyond earthquakes to include risks such as floods, landslides, hurricanes, hailstorms, wildfires, and avalanches. This initiative is a pivotal response to the diverse hazards associated with Türkiye’s geographical and climatic characteristics.
Following the technical visits in the affected areas of flood damage in the Black Sea region in August 2021, studies for flood tariff and landslide tariff started with a project team of academicians, actuaries, insurance professionals and specialists working on these subjects, and loss adjusters. It is considered that the experiences gained from field visits would be directive and highly beneficial for TCIP’s works on the subject.
For the flood tariff studies and the creation of a Flood Hazard Model; the existing Flood Water Depth Maps, Flood Hazard Maps, and Flood Risk Maps which are prepared within the scope of Flood Management Plans of Türkiye were provided by the General Directorate of Water Management under the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Using these maps, combined with vulnerability curves, average annual loss rates are calculated at neighbourhood level. This localized approach ensures that risk assessments are accurate and reflect regional conditions, supporting fair and precise premium calculations.
Figure 1. Financial Loss Ratio levels for flood.
Source: TCIP.
For landslides, a similar methodology was applied, utilizing susceptibility maps and detailed inventory data from the Directorate of Disaster and Emergency Management (AFAD). These datasets facilitated neighbourhood-level loss rate estimations, creating a robust foundation for pricing the associated risks.
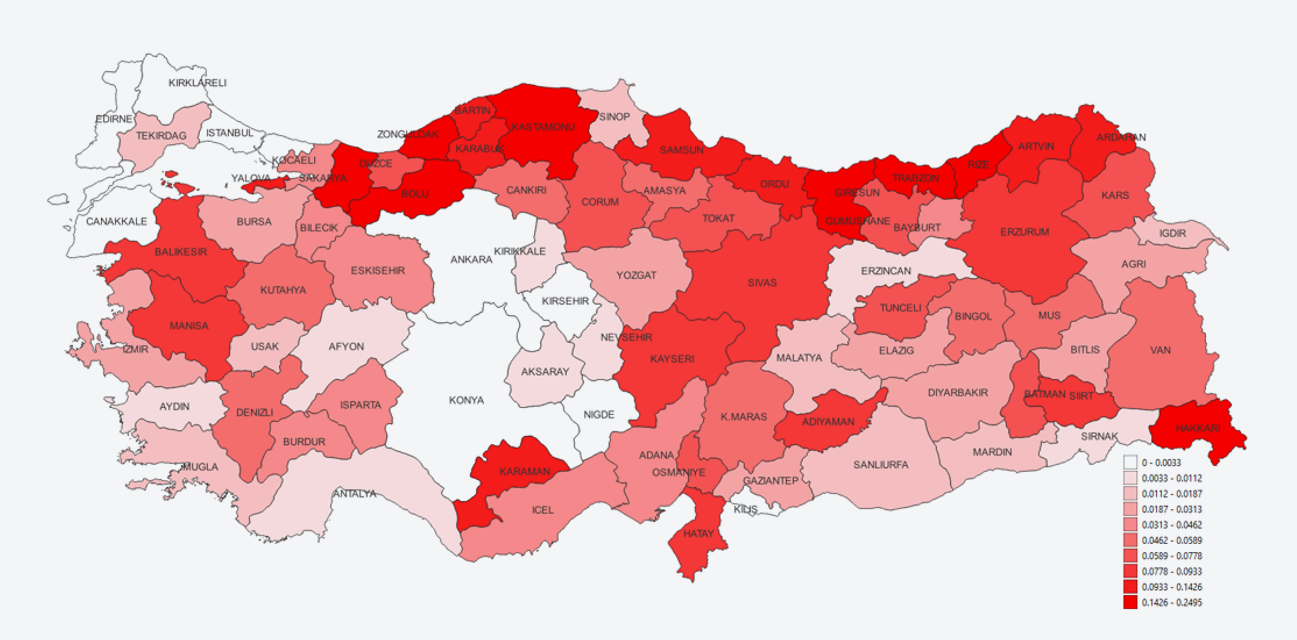
Figure 2. Financial Loss Ratio levels for Landslide.
Source: TCIP.
Actuarial studies followed the tariff calculations to finalize premium rates for floods and landslides. A risk-based model with five risk categories for each district was adopted, mirroring the structure used for compulsory earthquake insurance. This tiered approach aligns premiums with risk levels, promoting equity and incentivizing localized risk mitigation.
For other hazards, including storms, wildfires, avalanches, and hailstorms, fixed-premium structure is introduced. Although less detailed than the risk-based model, this approach simplifies implementation while expanding coverage accessibility. It is planned to study the tariffs for storms, wildfires, avalanches, and hailstorms after going on live especially by integrating the claims data that TCIP will be facing then. Last but not least, it is also planned that our new policy will include sinkhole and meteorite falls in the coming years, following coverage studies.
In spite of the fact that there is no known active volcano in Türkiye, the general conditions for facultative earthquake insurance cover provides volcanic eruption risk, which TCIP’s existing compulsory earthquake cover does not include. The new policy will also act as first loss type, but with quite extended perils. For this reason and in order to leverage the coverage for residential dwellings, it is decided to add volcanic eruption peril into the earthquake cover provided by Compulsory Earthquake Insurance.
The compulsory disaster insurance program will also cover structural damage to buildings. Although at the beginning of the project, the aim was to include content especially for the newly introduced perils (except volcanic eruption as it is attached to earthquake), the studies with the insurance companies providing facultative cover showed that there are several technical complexities which cannot be solved easily. It is thus decided not to include “content” at inception, its inclusion being postponed for future studies.
Instead, the new policy will introduce a new cover that we have named ‘Immediate Needs Coverage’, designed to meet the urgent financial needs of the beneficiaries of insured dwellings who will be directly affected by natural catastrophes. This supplementary coverage is designed as financial support, and it will be capped at 10% of the sum insured value, and a maximum that will be defined some time before it comes into effect, providing timely and practical assistance.
During all these studies the regulator, the Insurance and Private Pension Regulation and Supervision Agency (SEDDK), joined forces with TCIP and the insurance companies via association to revise and align the general conditions of fire insurance policies and related perils including earthquake and volcanic eruption. This will also provide smooth transactions between TCIP and insurance companies during claims operations.
Compulsory disaster insurance is aimed to play a vital role in strengthening community resilience and facilitating post-disaster recovery. Providing financial support will help affected individuals rebuild their lives and mitigate the economic burdens of disasters. This framework ensures a structured, equitable, and sustainable approach to managing the growing risks posed by natural hazards. Following its launch, TCIP aims to make further efforts to increase penetration in order to provide insurance cover with affordable premiums.
